💯 R Best Practices
How to set up a reproducible and collaborative workflow
Index
- 🚧 Project Configuration
- ✨ Tips and Tricks
- ♻️ Reproducible Workflow
- 🌐 Follow Standards
🚧 Project Configuration
Code smells, projects and scaffolding
🚧 Project Configuration
🚩 Dont’s
Important
This does not reset the workspace: all it does is delete user-created objects from the global workspace.
• Any packages that have ever been attached via library() are still available.
• Any options that have been set to non-default values remain that way.
• Working directory is not affected.
🚧 Project Configuration
✔️ Do’s
- You should always reason in terms of sessions, not workspace: don’t be afraid to use
Restart R Session(shift + cmd + 0).
🚧 Project Configuration
✔️ Do’s
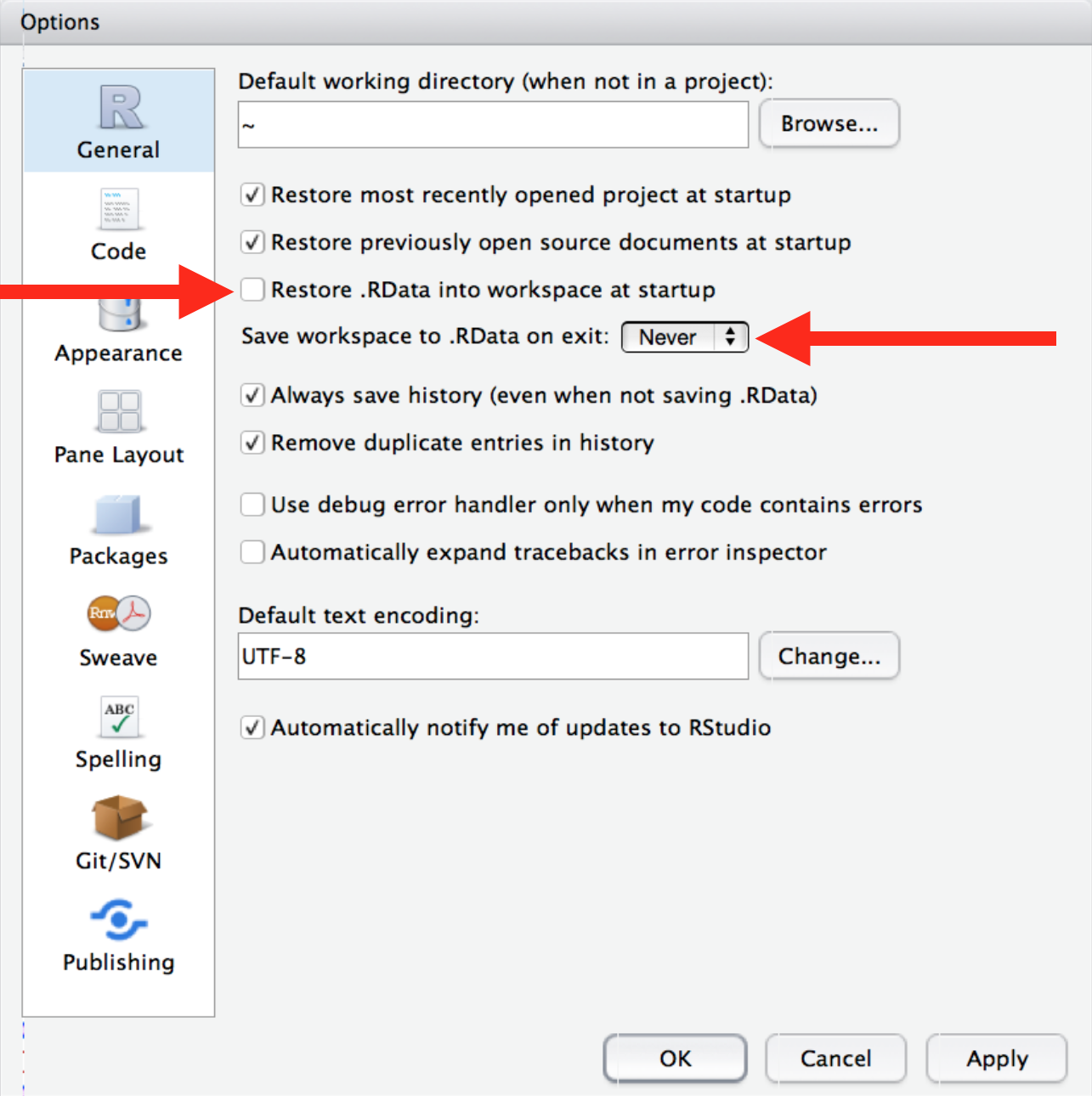
• When you quit R, do not save the workspace to an .Rdata file.
• When you launch, do not reload the workspace from an .Rdata file.
• In RStudio, set this via Preferences > Options > General.
🚧 Project Configuration
🚩 Dont’s
setwd("/Users/jenny/cuddly_broccoli/verbose_funicular/foofy/data")
- The chance of the
setwd()command having the desired effect – making the file paths work – for anyone besides its author is 0%. - It’s also unlikely to work for the author one or two years or computers from now.
- Hard-wired, absolute paths, especially when sprinkled throughout the code, make a project brittle.
🚧 Project Configuration
✔️ Use Projects
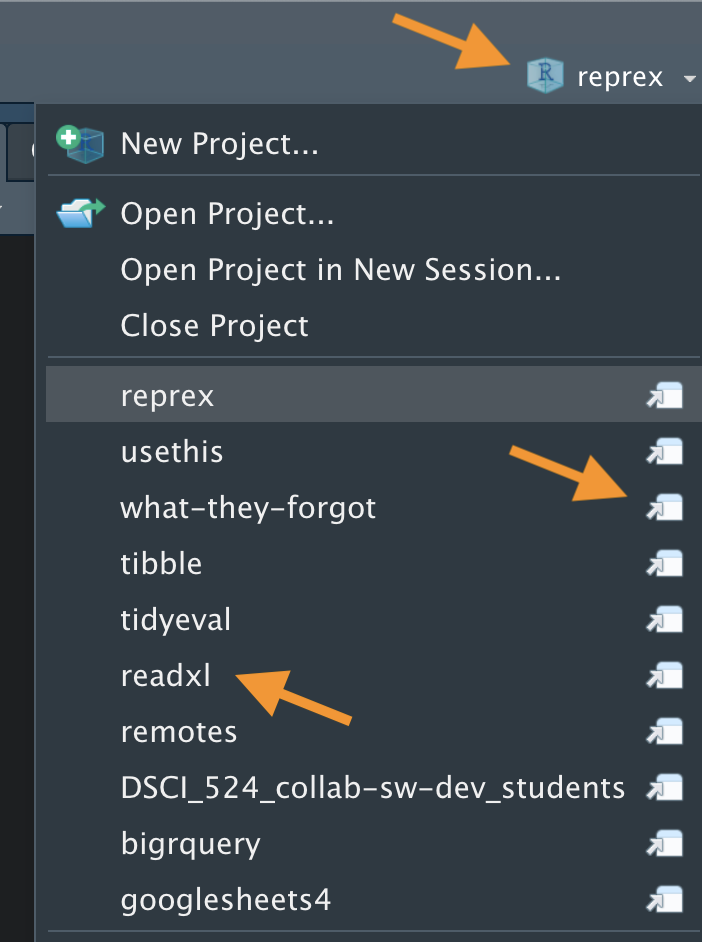
• Create a project with the top-left icon next to New file, or from the Command Palette.
• Open and manage Projects from the top-right drop-down menu.
• You can also open projects by double clicking on the *.Rproj file in your filesystem.
🚧 Project Configuration
✔️ Use {here}
🚧 Project Configuration
🎁 Extra
- Give meaningful names to variables. Stop saving each dataframe as
df.
“There are only two hard things in Computer Science: cache invalidation and naming things.”
✨ Tips and Tricks
Filenames, commands and documentation
✨Tips and Tricks
📁 File names should be
- machine readable: no spaces, no accents, no punctuation, no special characters, all lowercase.
- human readable.
- play well with default ordering.
Warning
Avoid / and \ for file names especially!
✨Tips and Tricks
📁 File names should be
- Use
_to delimit words. - Use
-to delimit meta-data fields. - Use dates and numbering to enforce ordering.
Example
2022_11_05-lecture_01-r_best_practices
✨Tips and Tricks
📁 File names should be
Example
01-helper-data-loading.R
02-helper-data-visualisation.R
03-helper-ml-model_tuning.R
- Split the code across different scripts, rather than maintaining an expensive monolith. In this way, you will only have to re-run the parts you actually need.
✨Tips and Tricks
📁 Project structure
- If the number of scripts grows, create sub-directories using the same naming criteria.
- There are many ways to structure a directory tree. For simplicity, you might want to start with:
.
├── .Rproj.user
├── data
│ ├── external # external data that does not belong to raw
│ ├── interim # intermediate manipulations
│ ├── processed # final data used for analysis/models
│ └── raw # raw data should never change!
├── reports # notebooks with analysis and exploration
├── src # contains the source code, also named `R`
├── your-proj.Rproj # ❗Project file
└── README.md # info about the project✨Tips and Tricks
⚙️ Commands
cmd + shift + Pcalls the command palette: from there, you can call any command.- Get help about any function:
✨Tips and Tricks
📚 Documentation
- Use
vignettes:
A vignette is like a book chapter or an academic paper: it can describe the problem that your package is designed to solve, and then show the reader how to solve it.
- You can see all the installed vignettes with
browseVignettes()and view one withvignette('your-vignette').
♻️ Reproducible Workflow
Use {renv} to create and manage virtual environments
♻️ Reproducible Workflow
📦 Virtual environments
- Are self-contained, isolated boxes to run code independently from the other libraries installed on your computer.
- i.e., this encapsulates local packages (vis-à-vis global ones).
- Provides all the details to exactly reproduce the environment you are writing your code into (starting from specific package versions).
♻️ Reproducible Workflow
📦 Virtual environments
- Install
{renv}:install.packages('renv') - Create a new
Project. - Run
renv::init(): this will initialise a new environment- and create a
renv/folder, as well as arenv.lock(which contains the details about every library you use).
- and create a
- Keep installing packages with
install.packages()(which is actually callingrenv::install()under the hood).
🌐Follow Standards
🌐Follow Standards
🔍 Linting
- Use
{lintr}as a static analysis tool:
It checks for adherence to a given style, identifying syntax errors and possible semantic issues, then reports them to you so you can take action.
- It also enforces the tidyverse style guide 👀
🌐Follow Standards
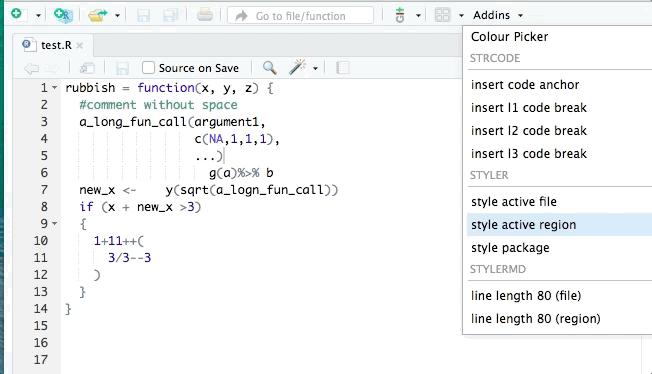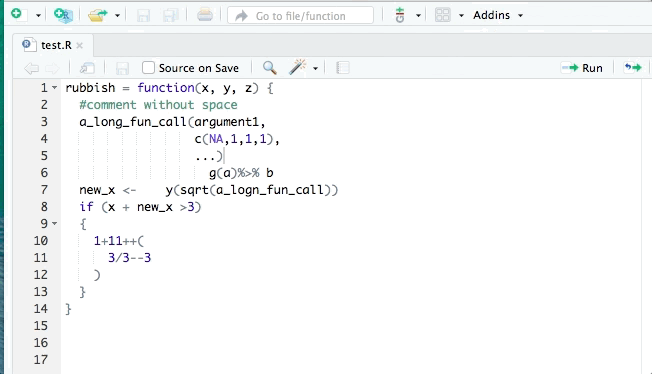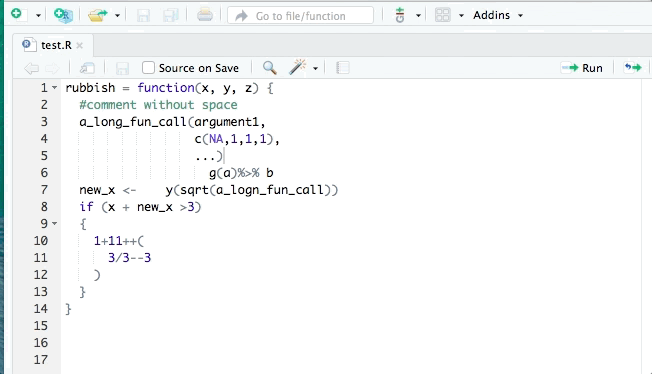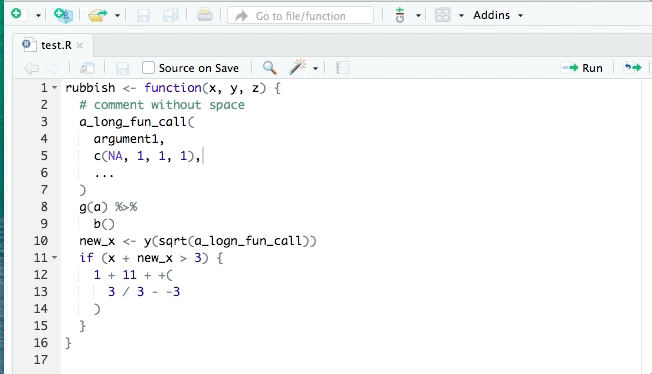
🪄 Formatters
- Use
{styler}
🌐Follow Standards
🪄 Formatters
- If you are using
git(you should) and GitHub, you can use GitHub Actions to build a continuous integration (CI) pipeline:
- Install the
{usethis}package. - Run
usethis::use_github_action('lint'). - Run
usethis::use_github_action('style').
- These commands will generate the configurations to run
{lintr}and{styler}, inside.github/workflows.
UniMi • Coding for Data Science and Data Management • AY 2022/2023